B) Nutritional value of indigenous leafy vegetables in Bintulu and Miri Sarawak
 Introduction:
Introduction:
This research group focuses on investigating wild or locally grown plant that have potential for food crops or other potential such as medicinal or industrial crops. We work on the various plant research such as ethnobotanical, agronomic, biology and ecology, nutritional value and propagation study.
Nutritional value of indigenous leafy vegetables in Bintulu and Miri Sarawak
Vegetable represents s significant group of food crops supplying important sources of vitamins and minerals in the daily diets of Malaysian. Indigenous vegetable can be defined as wild plant, uncultivated plant, cultivated plant, traditional and under-utilized vegetable to urban compared to native people. Rural people in many countries continue to consume wild and semi- wild plants in their diets. Indigenous vegetables in natural environement possess high nutritive value such as vitamins and minerals. While anti-nutrient is chemically active substances and often found in some edible plants. It appears to be toxic at high levels and some can bind to nutrients, thus when consumed will prevet their digestion and utillization of the body. There is only limited data to prove that wild leafy vegetables contain high levels of anti-nutritional substances. Many wild plants used in industrialized countries today were originally identified and developed through indigenous knowledge. Generally, in Malaysia most of studies of wild or indigenous fruit and vegetables are recorded in Peninsular Malaysia. In Sarawak, reports pertaining on utilization and marketable of indigenous vegetables were documented by Voon et al. (1990), Muhd Arif Shaffiq, (2013) and Noorasmah (2014). However, those studies have not given due to attention in terms of their whole nutiritional content i.e., proximate composition, mineral, vitamin, and anti-nutrient content. Due to their abundance, attribute qualities and cheap vegetables, create an interest in the study of nutritional anti-nutritional value and selected known and lesser known indigenous leafy vegetables. The objective of this study is to determine the consuming methods of indigenus leafy vegetables used by local community in Bintulu, Sarawak and to evaluate their nutritional, anti-nutritional content and propagation methods. The nutritional information of these indigenous vegetable will be used for advocating their increased utilization as vegetable crops. This project is funded by Universiti Putra Malaysia under the Inisiatif Putra Siswazah – Geran Putra (Project No GP-IPS/2016/9497100).

Pictures:
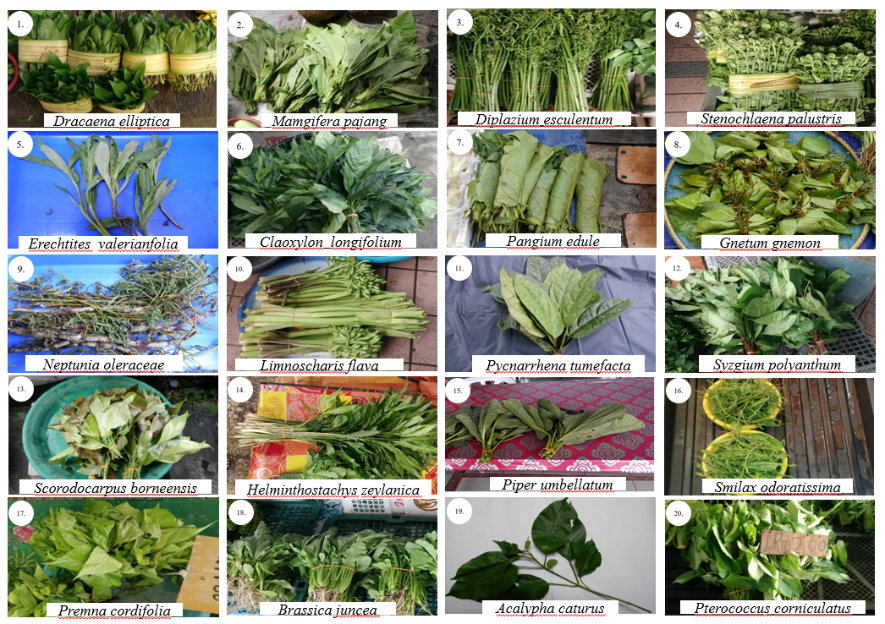

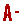
Figure 1 : Indigenous leafy vegetables in Bintulu Sarawak
 Publication
Publication
 Journal
Journal
- Saupi, N., Saidin, A.A, Ya, M.H.Z. and Sarbini, S.R. Diversity, utilization, and proximate composition of indigenous leafy vegetables consumed in Malaysia. 2019. Journal of Agriculture Food and Development. 5: 1-8.
- Ainul Asyira, S., Noorasmah, S., Sarbini, S.R., and Muta Harah, Z. 2016. Mineral content of five indigenous leafy vegetables from bintulu market, Sarawak Malaysia. Journal of Medicinal Herbs and Ethnomedicine. 2: 26 – 35
- Ainul Asyira Saidin, Noorasmah Saupi, Shahrul Razid Sarbini and Muta Harah Zakaria. 2017. Review on Nutritional Value of Indigenous Leafy Vegetables in Sarawak. In Natural Resources and Biodiversity Vol. 2. Nur Ashikin Psyquay Abdullah, Shahrul Razid Sarbini and Ahmed Osumanu Haruna (Eds.). pp. 104 – 116. Serdang: Universiti Putra Malaysia Press. ISBN 978-967-344-665-0
- Ainul Asyira Saidin, Noorasmah Saupi, Shahrul Razid Sarbini and Muta Harah Zakaria. Mineral and anti-nutrient contents of selected Sarawak local leafy vegetables. 2016. Presented at the 13th Universiti Malaysia Terengganu International Annual Symposium on Sustainability Science and Management (UMTAS2016). 13 – 15th December 2016. Primula Beach Hotel.
- Noorasmah, Saupi, Ainul Asyira Saidin, Muta Harah Zakaria@Ya and Shahrul Razid Sarbini. Indigenous Leafy Vegetables of Bintulu, Sarawak. Presented at the International Scientific Conference on Indigenous Crops 2018. “Potential Indigenous Plants for Commercialization”. 16th – 17th October 2018. Hilton Hotel, Kuching Sarawak.
- Ainul Asyira Saidin, Noorasmah, Saupi, Muta Harah Zakaria@Ya and Shahrul Razid Sarbini. 2018. Nutritional Values of Selected Wild Leafy Vegetables Consumed by Local People in Bintulu, Sarawak. Presented at the International Scientific Conference on Indigenous Crops 2018. “Potential Indigenous Plants for Commercialization”. 16th – 17th October 2018. Hilton Hotel, Kuching Sarawak
- Noorasmah, S., Ainul Asyira Saidin and Shiamala Devi Ramaiya. Underutilized Borneon leafy Vegetable, Dracaena gracilis Wall.: Proximate, minerals, anti-oxidants and anti-nutritional properties. Presented at The Southeast Asia Vegetable Symposium 2019 (SEAVEG 2019). 9 – 11th July. Hatten Hotel. Malacca, Malaysia
 For more further enquiries:
For more further enquiries:
Dr. Noorasmah Binti Saupi
Senior Lecturer
Department of Crop Science
Faculty of Agricultural Science and Forestry
Tel: +6086 855394
Email: noorasmah@upm.edu.my
Updated:: 21/08/2020 [lanz]
MEDIA SHARING






 Introduction:
Introduction:

 Publication
Publication Journal
Journal For more further enquiries:
For more further enquiries:


















